Administration
Menu Items
The OpenIddict page allow the following items under the “Administration” menu item:
- Applications: Application management page.
- Scopes: Scope management page.
Pages
Application Management
Applications page is used to manage applications. An application represent hosted applications that can request tokens from Ozdentity.com server.
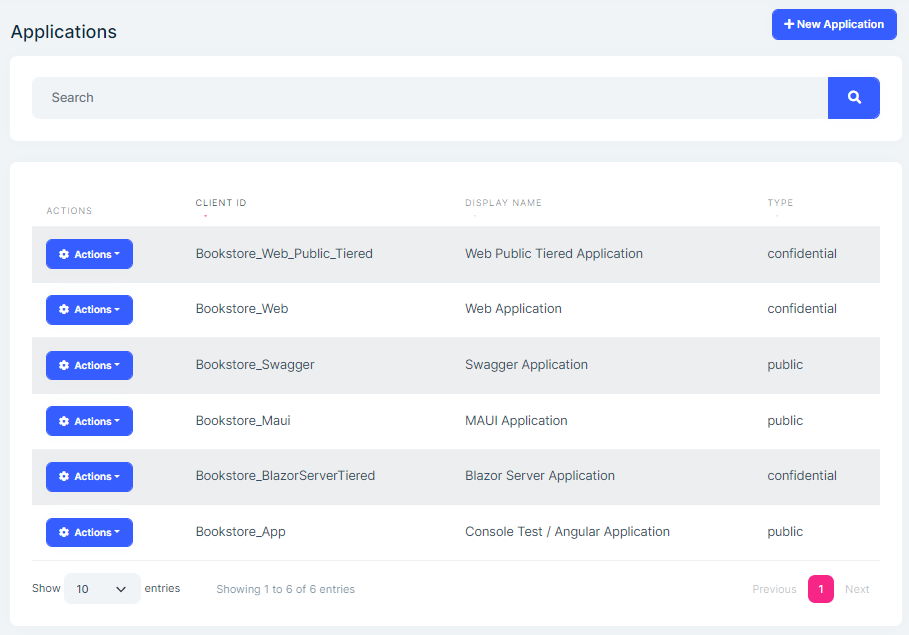
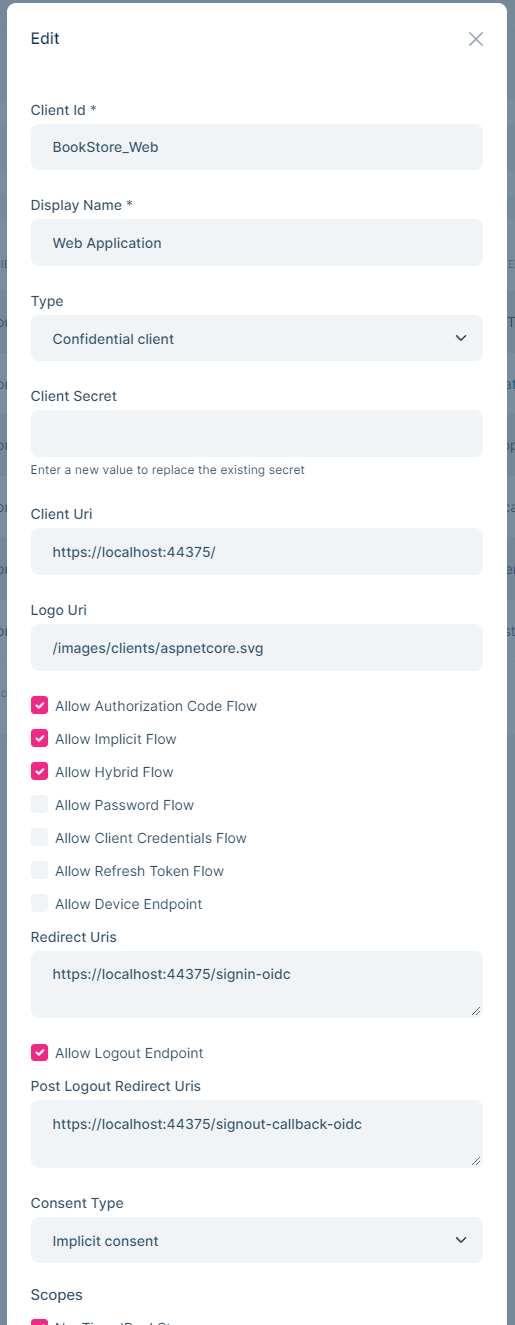
You can create new application or edit existing applications in this page:
API Scope Management
Scope page allows to manage API scope. To allow applications to request access tokens for APIs, you need to define API scopes.
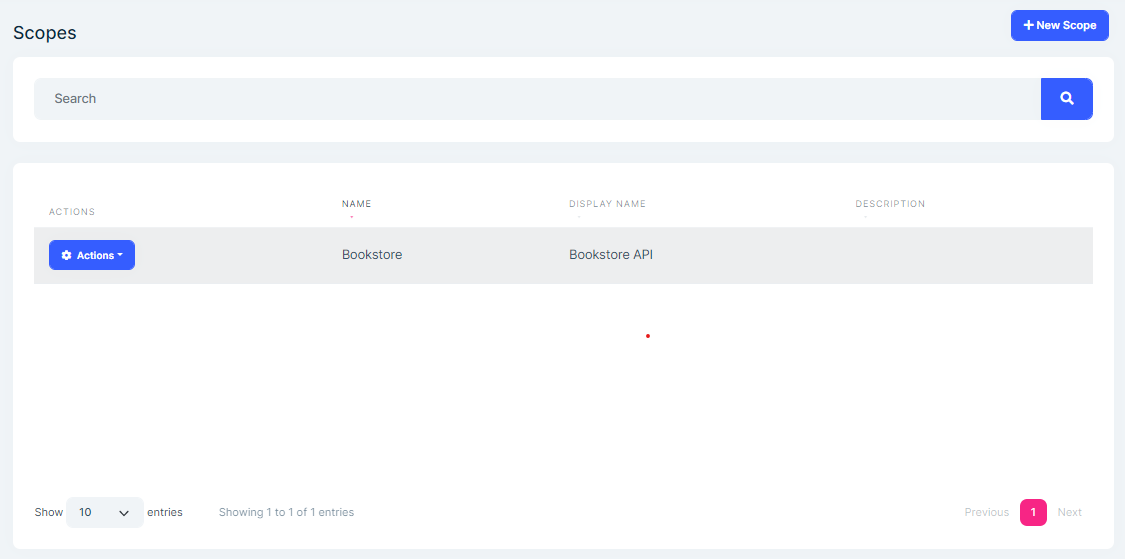
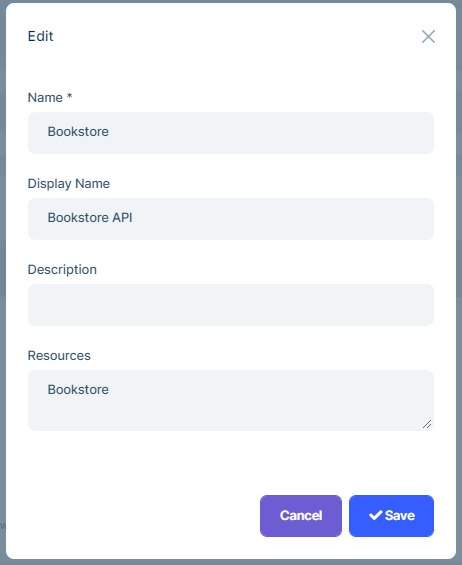
You can create a new API resource or edit an existing API resource in this page:
OpenIddictApplication
This section represent the applications that can request tokens from your OpenIddict Server.
OpenIddictApplications(aggregate root): Represents an OpenIddict application.ClientId(string): The client identifier associated with the current application.ClientSecret(string): The client secret associated with the current application. Maybe hashed or encrypted for security reasons.ConsentType(string): The consent type associated with the current application.DisplayName(string): The display name associated with the current application.DisplayNames(string): The localized display names associated with the current application serialized as a JSON object.Permissions(string): The permissions associated with the current application, serialized as a JSON array.PostLogoutRedirectUris(string): The logout callback URLs associated with the current application, serialized as a JSON array.Properties(string): The additional properties associated with the current application serialized as a JSON object or null.RedirectUris(string): The callback URLs associated with the current application, serialized as a JSON array.Requirements(string): The requirements associated with the current applicationType(string): The application type associated with the current application.ClientUri(string): URI to further information about client.LogoUri(string): URI to client logo.
OpenIddictAuthorization
OpenIddictAuthorizations are used to keep the allowed scopes, authorization flow types.
OpenIddictAuthorization(aggregate root): Represents an OpenIddict authorization.ApplicationId(Guid?): The application associated with the current authorization.Properties(string): The additional properties associated with the current authorization serialized as a JSON object or null.Scopes(string): The scopes associated with the current authorization, serialized as a JSON array.Status(string): The status of the current authorization.Subject(string): The subject associated with the current authorization.Type(string): The type of the current authorization.
OpenIddictScope
OpenIddictScopes are used to keep the scopes of resources.
OpenIddictScope(aggregate root): Represents an OpenIddict scope.Description(string): The public description associated with the current scope.Descriptions(string): The localized public descriptions associated with the current scope, serialized as a JSON object.DisplayName(string): The display name associated with the current scope.DisplayNames(string): The localized display names associated with the current scope serialized as a JSON object.Name(string): The unique name associated with the current scope.Properties(string): The additional properties associated with the current scope serialized as a JSON object or null.Resources(string): The resources associated with the current scope, serialized as a JSON array.
OpenIddictToken
OpenIddictTokens are used to persist the application tokens.
OpenIddictToken(aggregate root): Represents an OpenIddict token.ApplicationId(Guid?): The application associated with the current token.AuthorizationId(Guid?): The application associated with the current token.CreationDate(DateTime?): The UTC creation date of the current token.ExpirationDate(DateTime?): The UTC expiration date of the current token.Payload(string): The payload of the current token, if applicable. Only used for reference tokens and may be encrypted for security reasons.Properties(string): The additional properties associated with the current token serialized as a JSON object or null.RedemptionDate(DateTime?): The UTC redemption date of the current token.Status(string): The status of the current authorization.ReferenceId(string): The reference identifier associated with the current token, if applicable. Only used for reference tokens and may be hashed or encrypted for security reasons.Status(string): The status of the current token.Subject(string): The subject associated with the current token.Type(string): The type of the current token.
Request/Response Process
The OpenIddict.Server.AspNetCore adds an authentication scheme(Name: OpenIddict.Server.AspNetCore, handler: OpenIddictServerAspNetCoreHandler) and implements the IAuthenticationRequestHandler interface.
It will be executed first in AuthenticationMiddleware and can short-circuit the current request. Otherwise, DefaultAuthenticateScheme will be called and continue to execute the pipeline.
OpenIddictServerAspNetCoreHandler will call various built-in handlers (handling requests and responses), And the handler will process according to the context or skip logic that has nothing to do with it.
Example of a token request:
POST /connect/token HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type=password&
client_id=App&
client_secret=1q2w3e*&
username=admin&
password=1q2w3E*&
scope=API offline_access
This request will be processed by various handlers. They will confirm the endpoint type of the request, check HTTP/HTTPS, verify that the request parameters (client. scope, etc) are valid and exist in the database, etc. Various protocol checks. And build a OpenIddictRequest object, If there are any errors, the response content may be set and directly short-circuit the current request.
If everything is ok, the request will go to our processing controller(eg TokenController), we can get an OpenIddictRequest from the HTTP request at this time. The rest will be based on this object.
Check the username and password in the request. If it is correct create a ClaimsPrincipal object and return a SignInResult, which uses the OpenIddict.Validation.AspNetCore authentication scheme name, will calls OpenIddictServerAspNetCoreHandler for processing.
OpenIddictServerAspNetCoreHandler do some checks to generate json and replace the http response content.
The ForbidResult ChallengeResult are all the above types of processing.
If you need to customize OpenIddict, you need to replace/delete/add new handlers and make it execute in the correct order.
Please refer to: https://documentation.openiddict.com/guides/index.html#events-model
PKCE
Setting Tokens Lifetime
Update PreConfigureServices method of AuthServerModule (or HttpApiHostModule if you don’t have tiered/separate-authserver) file:
PreConfigure(builder =>
{
builder.SetAuthorizationCodeLifetime(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(30));
builder.SetAccessTokenLifetime(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(30));
builder.SetIdentityTokenLifetime(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(30));
builder.SetRefreshTokenLifetime(TimeSpan.FromDays(14));
});
Refresh Token
To use refresh token, it must be supported by OpenIddictServer and the refresh_token must be requested by the application.
Configuring OpenIddictServer
There are two ways to allow an application to use the refresh_token.
From OpenIddictDataSeedContributor, add
OpenIddictConstants.GrantTypes.RefreshTokento grant types inCreateApplicationAsyncmethod:await CreateApplicationAsync( ... grantTypes: new List //Hybrid flow { OpenIddictConstants.GrantTypes.AuthorizationCode, OpenIddictConstants.GrantTypes.Implicit, OpenIddictConstants.GrantTypes.RefreshToken, }, ...Note: You need to re-create this client if you have generated the database already.
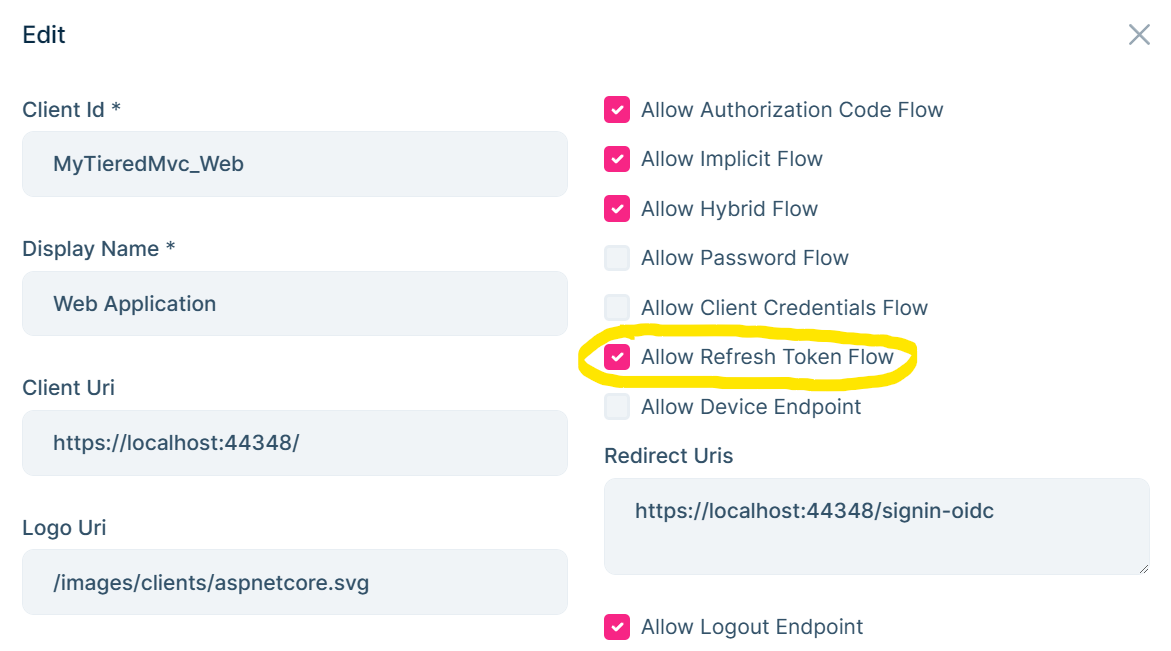
Or from OpenIddict Management UI, edit your application and
Allow Refresh Token Flow:
Note: Angular application is already configured to use
refresh_token.
Configuring Application:
You need to request the offline_access scope to be able to receive refresh_token.
In Razor/MVC, Blazor-Server applications, add options.Scope.Add(\"offline_access\"); to OpenIdConnect options. These application templates are using cookie authentication by default and has default cookie expire options set as:
.AddCookie(\"Cookies\", options =>
{
options.ExpireTimeSpan = TimeSpan.FromDays(365);
})
Cookie ExpireTimeSpan will ignore access_token expiration and expired access_token will still be valid if it is set to higher value than the refresh_token lifetime. It is recommended to keep Cookie ExpireTimeSpan and the Refresh Token lifetime same, hence the new token will be persisted in the cookie.
In Blazor wasm applications, add options.ProviderOptions.DefaultScopes.Add(\"offline_access\"); to AddOidcAuthentication options.
In Angular applications, add offline_access to oAuthConfig scopes in environment.ts file. (Angular applications already have this configuration).